Introduction to Around
Demo: http://recordit.co/awrQb1zn2I
Around: a Geo-index based social network
• Built a scalable web service in Go to handle posts and deployed to Google Cloud (GAE flex) for better scaling
• Utilized ElasticSearch (GCE) to provide geo-location based search functions such that users can search nearby posts within a distance (e.g. 200km)
• Used Google Dataflow to implement a daily dump of posts to BigQuery table for offline analysis
• Aggregated the data at the post level and user level to improve the keyword based spam detection (BigQuery)
Create a new cloud project.
Step 2.1.1 Open https://console.cloud.google.com/ and sign in with your gmail account.
Choose Sign up for free trial, enter a credit card (Must do). GCP has $300 discount for new users, which is enough for project purpose.
Step 2.1.2 Click ‘My Project’. Create a new Project called ‘Around’. Google Cloud will automatically generate a new project id for you.
Geo-Index and ElasticSearch
how to perform 1-d range search? For example, given a 1-d binary search tree, find all the values between [3, 18].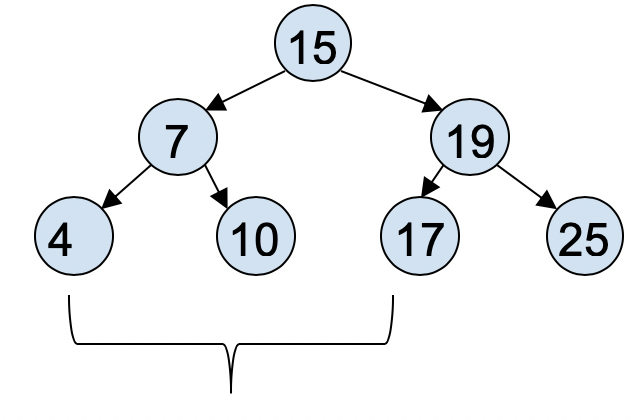
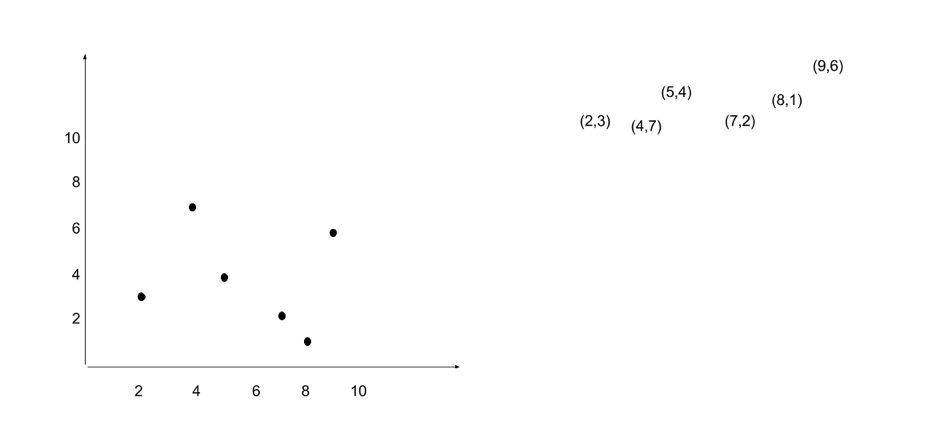
What about 2d data?
- Geo index: lat between [10.2, 10.3] and lon between [120.0, 120.5]
- Price between [$10, $100], date between [Jan-01-2017, Jun-01-2017]
- Weight between [120pb,140pb], height between [150cm, 180cm]
- …
K-D tree is one implementation to solve such k-dimensional search problem.
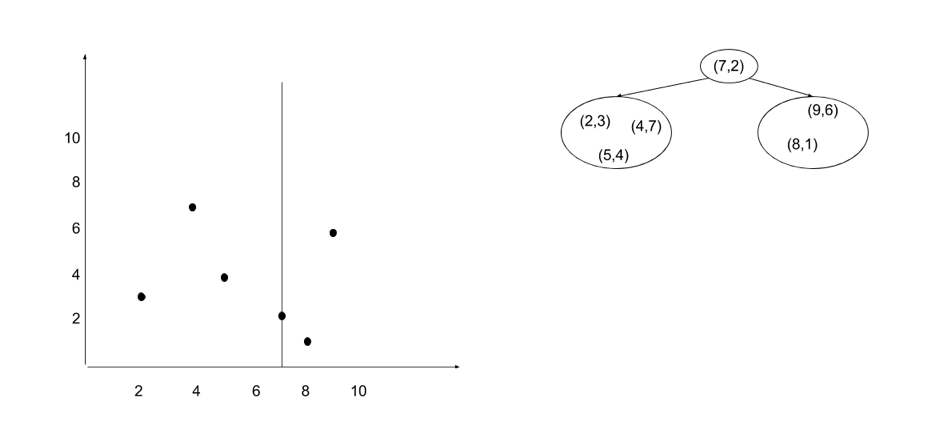
Then we choose one median point and split the space into two parts horizontally.
Continue to split them into more parts (vertically)
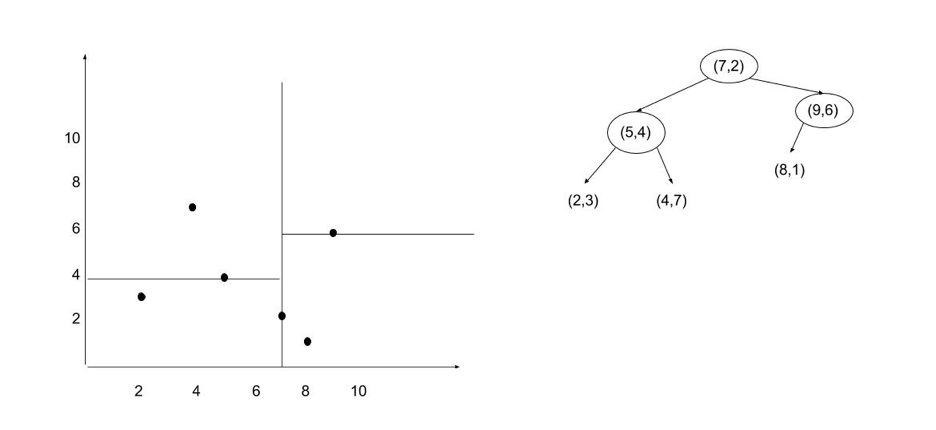
Question: how to find all the points within a Range (R)?
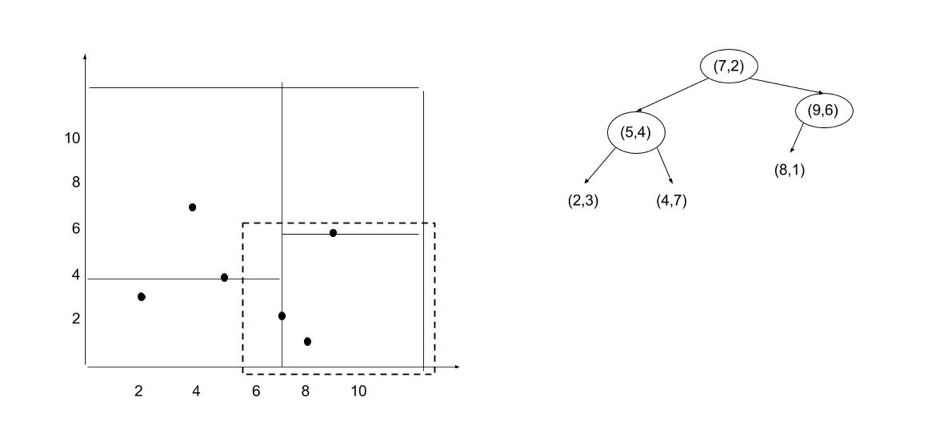
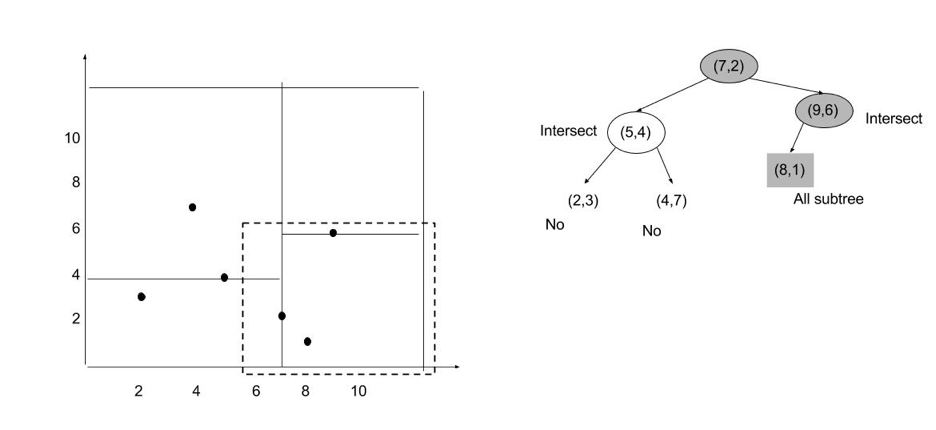
Range Search Algorithm:
- If query box doesn’t overlap bounding box, stop recursion
- If bounding box is a subset of query box, report all the points in current subtree
- If bounding box overlaps query box, recurse left and right
ELK (ElasticSearch, Logstash and Kibana)
Elasticsearch is an open source, distributed, RESTful search engine. As the heart of the Elastic Stack, it centrally stores your data so you can query the data quickly.
SQL is slower. Since ELK uses a pair to search directly.
1 | SELECT * FROM LOCATIONS WHERE lat <= 12 AND lat >= 10 AND lon >= 120 AND lon <= 130 |
Google Compute Engine (GCE)
Cloud Model
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
Offers virtual machines (Xen, KVM, VirtualBox, VMware ESX, etc.). Amazon EC2 and Google Compute Engine belong to IaaS as well.
- PaaS (Platform as a service)
computing platform including programming language execution environment, database and web server. Develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing hardware and software layers Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine
- SaaS (Software as a service)
users are provided access to application software and databases.
Google Apps, GoToMeeting
The overall structure (tech stack) of our project:
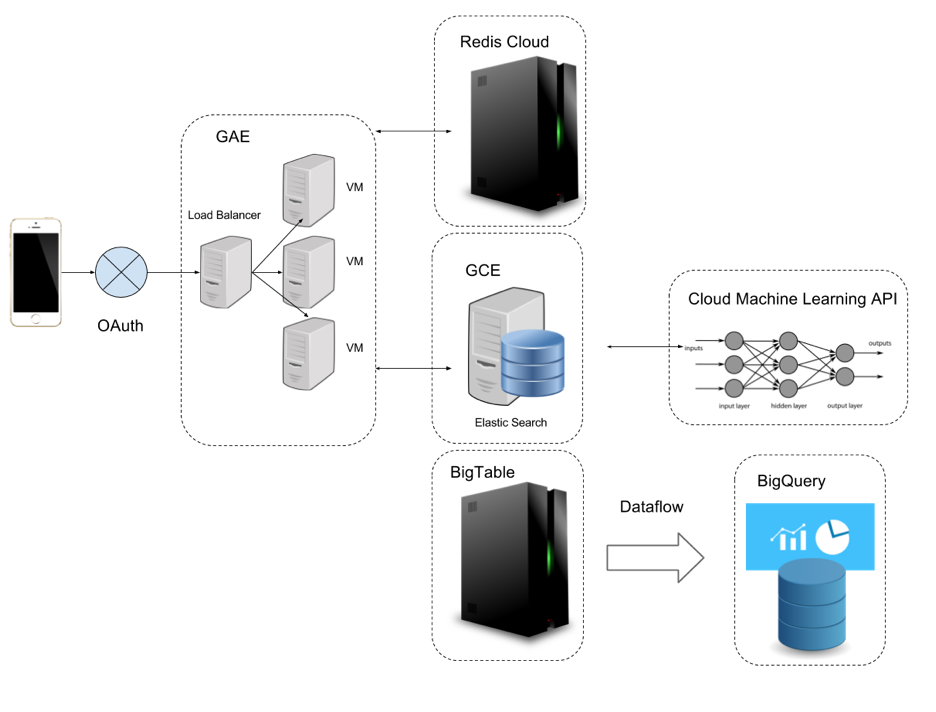
Question: why we need such a complicated infrastructure
Answer: because in industry, we need to handle very different requirements compared to in school.
Configure
Find NETWORKING -> VPC network -> Firewall rules
Click CREATE FIREWALL RULE
In the next page, give it a name like ‘elasticsearch’. Set the Target tags to be ‘es’, source IP ranges to be ‘0.0.0.0/0’, and the specified protocols and ports to be ‘tcp:9200’.
Wait until the firewall rules is created.
Find Compute Engine->VM instances
Choose ‘Change’ and switch to Ubuntu 16. Keep the size of 10GB is fine.
Then in the Networking -> Network tags, set it to be ‘es’ (the firewall rule that we created).
After one minute, you will see the instance is started. Choose ‘SSH’ and then ‘Open in browser window’.
In the terminal, enter
1 | sudo apt-get update |
It will install java to your vm. To verify, enter ‘which java’ and ‘java -version’ to check
Install ElasticSearch as below
1 | wget https://download.elastic.co/elasticsearch/release/org/elasticsearch/distribution/deb/elasticsearch/2.3.1/elasticsearch-2.3.1.deb |
Edit the configuration file
1 | sudo vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml |
Add two lines to the config, to allow all traffic and listen on port 9200.
1 | network.host: 0.0.0.0 |
Save this and Start ElasticSearch
1 | sudo service elasticsearch start |
Check the status of ElasticSearch1
sudo service elasticsearch status
You should be able to see ‘active’ in the status
Back to your console.cloud.google.com, find the public IP address(external)
Put the IP address and port together (:9200) in a new tab and see whether the server is on. The name or version might be different.
NOTE: Don’t use https! Should use http.
You should get something like this:
1 | { |
Which means your ES server is running as expected.
Update Go Code
Update handlerSearch
Original source of codes (https://olivere.github.io/elastic/)
In here we have to import source code of elastic.(v3)
1 | To get the package, execute: |
1 | func handlerSearch(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { |
Code explanation
Let’s explain these codes line by line1
client, err := elastic.NewClient(elastic.SetURL(ES_URL), elastic.SetSniff(false))
It means we create a connection to ES. If there is err, return.
1 | q := elastic.NewGeoDistanceQuery("location") |
Prepare a geo based query to find posts within a geo box.
1 | searchResult, err := client.Search(). |
Get the results based on Index (similar to dataset) and query (q that we just prepared). Pretty means to format the output.
1 | for _, item := range searchResult.Each(reflect.TypeOf(typ)) { |
Iterate the result in results which are type of Post (typ)
1 | p := item.(Post) |
Cast an item to Post, equals to p = (Post) item in java
1 | ps = append(ps, p) |
Add the p to an array, equals ps.add(p) in java
1 | js, err := json.Marshal(ps) |
Convert the go object(array) to a string1
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*")
Allow cross domain visit for javascript.
We also need to put ES library in import1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9import (
elastic "gopkg.in/olivere/elastic.v3"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"encoding/json"
"log"
"strconv"
"reflect"
)
Add const before main function
1 | const ( |
Replace YOUR_ES_IP_ADDRESS with your ES address (public IP).
Step 2.2.5 Open your terminal (Mac and Windows). Enter
1 | go get gopkg.in/olivere/elastic.v3 |
Once it is done, you won’t be able to see any more compile errors in Intellij. If it does not work (elastic is still red), try to restart it.
More readings
- Reflect type https://golang.org/pkg/reflect/
- ES in Go https://github.com/olivere/elastic
Step 2.2.6 In order to create index in ES, we need to update main
What’s mapping in ES? It tells you what’s the type of a variable if not default.
1 | func main() { |
1 | exists, err := client.IndexExists(INDEX).Do() |
Check if the index exists.
1 | mapping := `{ |
If not, create a new mapping. For other fields (user, message, etc.) no need to have mapping as they are default. For geo location (lat, lon), we need to tell ES that they are geo points instead of two float points such that ES will use Geo-indexing for them (K-D tree)
1 | _, err := client.CreateIndex(INDEX).Body(mapping).Do() |
Create this index
More readings
- ES in Go https://github.com/olivere/elastic
- Mapping in ES https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping.html
Step 2.2.7 Update handlerPost
Add external import of uuid
1 | import ( |
How to add a new document to the index?
https://github.com/olivere/elastic has an example
1 | // Add a document to the index |
Student Question: how to complete this one?
1 | func handlerPost(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { |
Step 2.2.8 Open terminal, enter
1 | go get github.com/pborman/uuid |
Make sure your ES_URL is updated from your aws instance in step 1.
Step 2.2.9 Run your main.go again
Errors
If you have such an error, your ES_URL is incorrect.
1 | panic: no Elasticsearch node available |
If you have such error, you have started two main.go, stop the other one.
1 | 2017/06/30 07:07:01 listen tcp :8080: bind: Only one usage of each socket address (protocol/network address/port) is normally permitted. |
If you have such error, you forgot to comment one line fmt.Fprintf(w, "Search received: %s %s %s", lat, lon, ran).
1 | Search received: %!s(float64=37.4) %... |
Step 2.2.10 Open Postman, find the post query from history. (POST, http://localhost:8080/post)
1 | { |
And then find the get query from history. (GET, url=http://localhost:8080/search?lat=37.5&lon=-120)
You should get the results back
1 | [ |
Post more examples with different locations and then get with different lat/lon to see how many results you may get. If you have zero result back and no error, probably your geo location is wrong.